Transistors
|
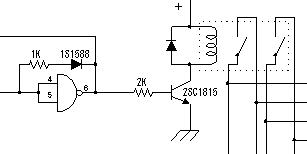
The transistor's finction is to amplify an electric current. Many different kinds of transistors are used in analog circuits, for different reasons. This is not the case for digital circuits. In a digital circuit, only two values matter; on or off. The amplification abilitiy of a transistor is not relevant in a digital circuit. In many cases, a circuit is built with integrated circuits(ICs). Transistors are often used in digital circuits as buffers to protect ICs. For example, when powering an electromagnetic switch (called a 'relay'), or when controlling a light emitting diode. (In my case.) Two different symbols are used for the transistor. PNP type
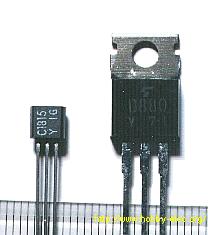 On the left in the photograph is a 2SC1815 transistor, which is good for use in a digital circuit. They are inexpensive when I buy them in quantity. In Japan it costs 2,000 yen for a pack of 200 pieces. (About 10 US cents/piece in 1998) On the right is a device which is used when a large current is to be handled. Its part number is 2SD880. The electrical characteristics of each is as follows.
Data sheet for 2SC1815 Because the component leads differ between kinds of transistors,
you need to confirm the leads with a datasheet, etc. 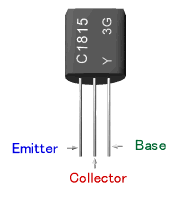 Example of 2SC1815 transistor Part number is printed on the flat face of the transistor, and indicates the front. Right side : Base Center : Collector Left side : Emitter 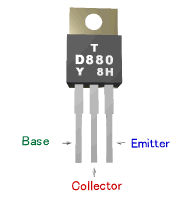 Example of 2SD880 transistor Part number is printed on the flat face of the transistor, and indicates the front. Right side : Emitter Center : Collector Left side : Base 2SC1815 is opposite. |