Japanese characters
 "Hiragana" is used like the English alphabet. All Japanese can be written in Hiragana, but we don't use it like that. Generally, they are used as characters which supplement the Kanji. Japanese sentences are different from English and don't use spaces between the words. So, it is very difficult to read when not using the kanji. The meaning in the kanji can be understood from the form of the character itself. There are 46 basic "Hiragana" characters. The kanji was introduced from China. It is called "Kanji" because it was introduced to Japan when China was called "Kan" in the past. "ji" means "character." "Hiragana" and "Katakana" are characters which were made, transforming the kanji. There are an enormous number of Kanji. More than thousands. I don't know all kanjis. Elementary school students (From 6 years old to 11 years old) in Japan learn 1006 kanjis. Most of the kanjis used in daily life are contained in these 1006 characters. 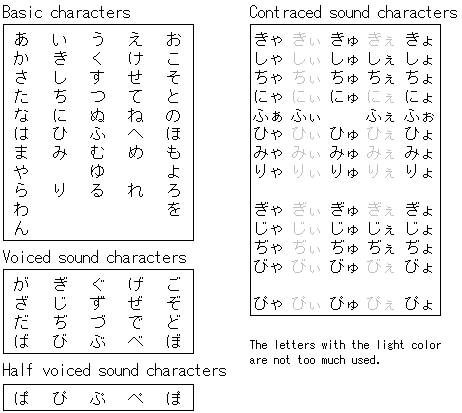 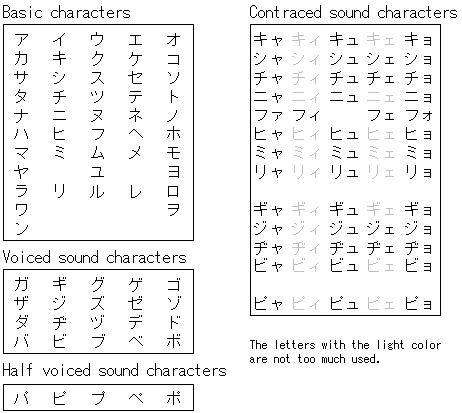 |